Daewoo Warehouse Forklifts Fresno
Definition of Forklift Classes
The forklift is used in many warehouse and retail settings for various daily task, including carrying heavy merchandise, stocking shelves and delivering loads of goods. Based on the Industrial Truck Association there are eight forklift classes. The machines are classified according to kind of engine or motor, kind of tires, and the way the equipment is steered. Forklifts are also called lift trucks.
Class I forklifts - Electric Motor Forklifts
These are regular electric motor lift trucks. Types of Class I forklift comprise the sit-down, three-wheeled varieties which are commonly used to transport pallets of mulch at home goods stores.
Class II forklifts - Narrow Aisle Electric Motor Lift Trucks
These trucks do not require much space to operate. Class II trucks consist of forklifts with swinging masts and side-loading models.
Class III forklifts - Electric Motor Hand Trucks
Class IV forklifts - Internal Combustion Engine Forklifts
These trucks have engines similar to those found in cars. They come with either cushion tires or solid tires. usually the back of the truck has a counterweight in order to make the machinery more stable.
Class V forklifts are like Class IV forklifts since both have internal combustion engines and are usually counterbalanced. The difference is in the tires that are used. Class V trucks utilize radial or pneumatic tires.
Tractors
Class VI forklifts - Towing Tractor Lift Trucks
These trucks are sit-down tractors that can lift bulky loads and pull loads weighing over 450 kilograms. These trucks can are available with either an an IC engine or an electric motor.
Class VII lift trucks - Rough Terrain Vehicles
This class of lift truck has internal combustion engines and pneumatic tires. They are normally employed in construction, logging and agriculture. These kind of trucks are recommended for worksites where the ground is uneven and rough and riddled with debris.
Class VIII forklifts - Manual Lift Trucks
These trucks are hand pallet lift trucks operated by a person who either pushes or pulls the vehicle. The forks are usually operated hydraulically, and have a low maximum lift height. This class includes personnel and burden carriers.
- Haulotte Knuckle Boom Lifts Fresno
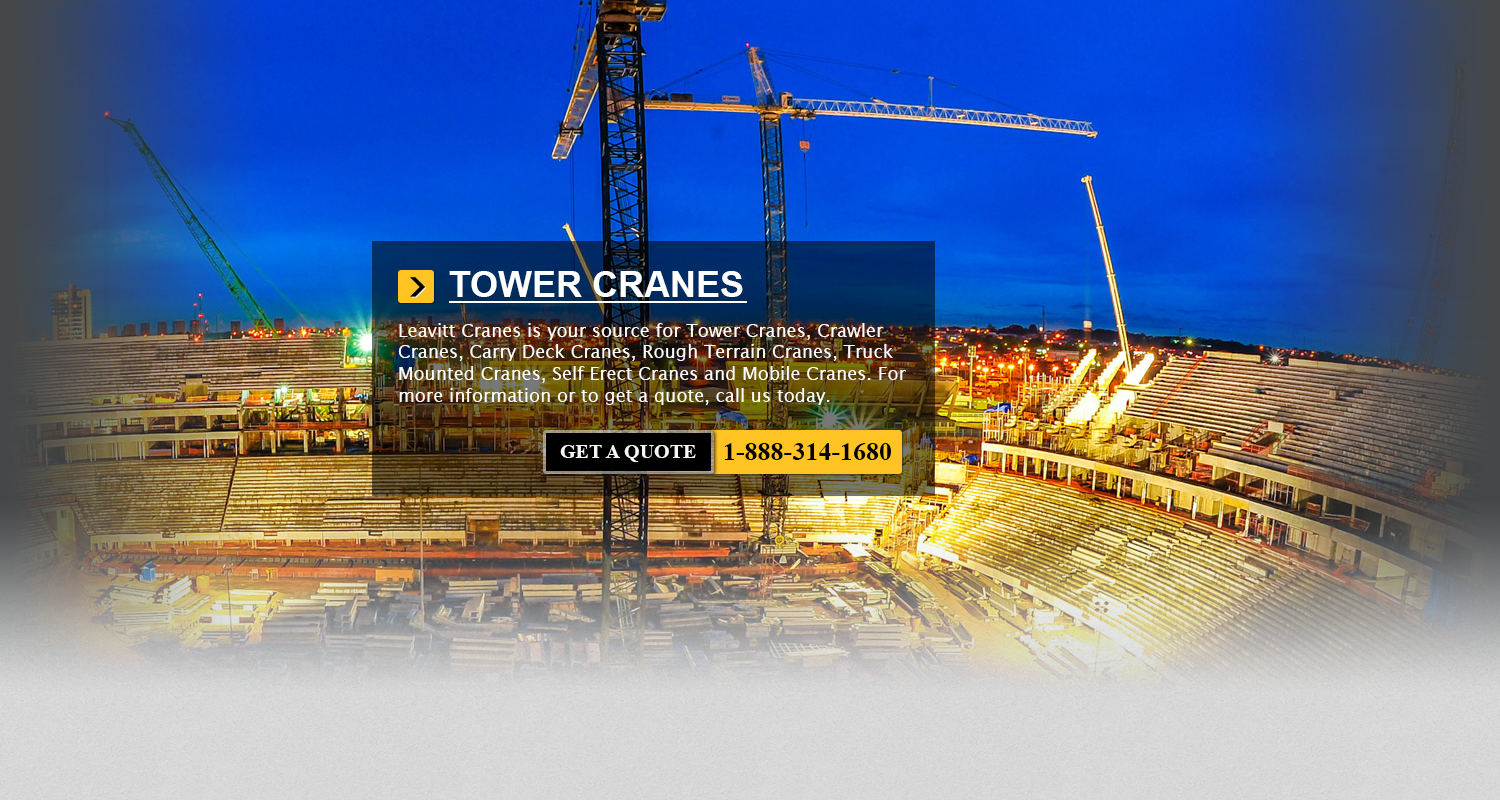
Knuckle Boom Crane Within Europe, Knuckle boom cranes have been extremely popular, since the roads are normally narrow. There are a lot greater restrictions on trucks within Europe than there are within North America too.... More - JCB Telehandlers Fresno
It doesn't matter where in the world you look, you would find a JCB machine. Proudly, JCB is amongst the top 3 manufacturers in the world of construction machinery. The company operates on 4 continents... More - Terex Articulated Man Lifts Fresno
Various Kinds of Aerial Lift A specialized type of heavy machinery which enables a person to be lifted into the air is aerial lifts. These machines are typically used to perform repairs on areas which... More - FM GRU Self Erecting Cranes Fresno
Self-Erecting Cranes The hydraulic portion of self-erecting cranes is extremely safe and fast. The steering axels offer minimum radius of curvature and this enables the cranes the ability to be placed into narrow spaces. Also,... More - SVE Truck Big Forklift Fresno
SVE provides a huge array of forklift units which are suited for lots of different uses. The smallest of the lift trucks is best suited for house factories, sawmills, and in concrete and stone factories.... More